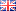
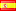
When it comes to power transmission, selecting the right cable is essential for ensuring efficiency and reliability in electrical systems. Among the various options available, All Aluminum Conductor (AAC) cables stand out for their unique properties.
Composed entirely of aluminum, AAC cables are commonly used for overhead power distribution, making them a staple in both urban and rural environments.
This blog post will delve into the advantages and disadvantages of these cables, providing a clear understanding of their applications and performance characteristics.
We’ll explore how their lightweight design and corrosion resistance can benefit projects, as well as the limitations they may impose in terms of conductivity and load capacity.
By the end, you will have a comprehensive overview of these cables, enabling you to make informed decisions when considering them for your electrical projects.
Whether you’re a utility professional, an engineer, or someone curious about electrical infrastructure, this guide will equip you with the necessary insights into it and their role in modern power distribution systems.
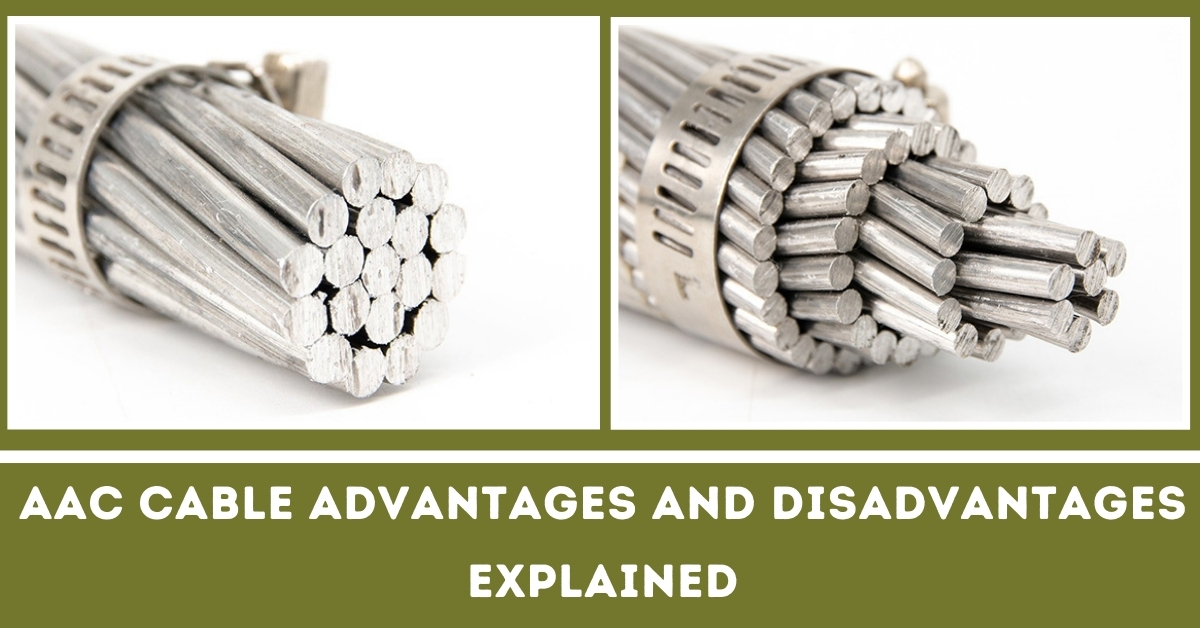
AAC, or All Aluminum Conductor Cable, is a type of electrical cable made entirely from aluminum. It is primarily designed for overhead power transmission and distribution applications.
Unlike other cable types that may use copper or a combination of materials, It’s utilize aluminum, which offers several unique benefits. The use of aluminum allows for a lightweight construction, making these cables easier to handle and install.
These are typically composed of multiple strands of aluminum wire twisted together to form a flexible conductor.
This design enhances the cable’s strength and flexibility, allowing it to withstand various environmental conditions. The construction of these cables is standardized to ensure reliability and efficiency in power transmission.
In terms of conductivity, aluminum has about 61% of the conductivity of copper. While this is lower, it is often sufficient for many applications, especially when the cables are designed for specific load requirements.
Additionally, the natural oxide layer on aluminum provides excellent resistance to corrosion, making these cables suitable for outdoor and humid environments.
Overall, these are widely used in the electrical industry due to their favorable characteristics, including cost-effectiveness and durability.
AAC (All Aluminum Conductor) cables come with several advantages that make them a preferred choice for overhead power transmission and distribution. Below are the key benefits of using it, along with detailed explanations of each advantage.
One of the most significant advantages of AAC cables is their lightweight construction. Aluminum is much lighter than copper, which allows for easier handling and installation.
The reduced weight of it means that utility companies can use lighter poles and supporting structures.
This can result in significant savings in materials and labor during installation, making it easier to transport and maneuver the cables in various settings.
The lightweight nature also minimizes the stress on supporting structures, reducing the likelihood of damage or failure.
It have excellent corrosion resistance due to the natural oxide layer that forms on aluminum when it is exposed to air. This protective layer prevents further oxidation and helps maintain the integrity of the conductor over time.
This property is particularly beneficial in environments exposed to moisture, pollution, or other corrosive elements.
Unlike copper, which can corrode when exposed to certain environmental conditions, This can withstand harsher climates, making them suitable for long-term outdoor applications.
This advantage means that it typically require less maintenance and have a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Cost is always a critical factor in any electrical project, and AAC cables are generally more affordable than copper alternatives.
The material cost of aluminum is lower than that of copper, and when combined with the savings from lighter structures and reduced installation costs, It become an attractive option for utility companies and contractors.
Lower initial costs make it suitable for large-scale projects, allowing for more budget-friendly solutions without compromising quality or performance.
This affordability can help utility companies pass savings on to consumers, ultimately benefiting the end-user.
While aluminum has lower conductivity than copper, AAC cables still provide decent electrical conductivity. The conductivity of aluminum is approximately 61% that of copper.
For many overhead power transmission applications, this level of conductivity is adequate, particularly when considering other factors such as installation costs and weight.
When designed correctly, It can effectively meet the demands of various load conditions, making them a reliable option for electrical distribution.
This balance of conductivity and affordability makes it a popular choice in the industry.
It can be manufactured with different configurations and strand counts, providing flexibility in design for various applications. Utility companies can customize these cables based on specific project requirements, such as the expected load, distance, and environmental conditions.
This adaptability means that it can be engineered for optimal performance in various settings, from urban to rural environments.
The ability to tailor cable specifications helps ensure that the electrical system can efficiently handle its operational demands while maintaining safety standards.
Aluminum has good thermal conductivity, which helps AAC cables manage heat dissipation effectively. During periods of high electrical load, cables generate heat due to electrical resistance.
Proper thermal management is essential for preventing overheating, which can lead to cable failure. These are designed to dissipate heat efficiently, allowing them to operate safely under normal conditions.
This characteristic is crucial in maintaining performance and reliability, especially during peak demand periods when the risk of overheating is higher.
Due to their inherent durability and corrosion resistance, It require less maintenance than other types of cables.
This low-maintenance aspect is particularly appealing to utility companies looking to reduce long-term operational costs.
The reduced need for inspections and repairs allows for more efficient use of resources, as companies can allocate their maintenance budgets to other critical areas.
This advantage also contributes to the overall reliability of the electrical distribution system, ensuring that power can be transmitted without frequent interruptions.
While aluminum is lighter than copper, it also has a good tensile strength that allows it to withstand mechanical stress. This strength is particularly important for overhead applications where cables are subjected to various environmental forces, such as wind, ice, and temperature changes.
The construction of these cables, often featuring multiple strands, enhances their ability to bear tension and reduces the risk of breakage.
This characteristic makes it suitable for long spans and challenging installations, providing peace of mind for utility companies and contractors.
Aluminum is a highly recyclable material, making it an environmentally friendly choice. Recycling aluminum requires significantly less energy compared to extracting and processing new aluminum from ore.
This sustainability aspect is increasingly important in today’s environmentally conscious society.
Utility companies and contractors looking to reduce their carbon footprint can benefit from choosing this, contributing to a greener future while meeting energy demands efficiently.
The lightweight nature of AAC cables not only facilitates easier handling but also simplifies the installation process.
Workers can quickly install AAC cables without the need for heavy lifting equipment, reducing the time and effort required for installation.
This efficiency is especially beneficial in remote or hard-to-access areas, where logistical challenges can arise.
Additionally, the ease of installation can lead to faster project completion, enabling utility companies to bring power to new areas more quickly.
In some cases, It may be preferred for their visual impact. The sleek appearance of aluminum can be more aesthetically pleasing than other cable types, particularly in urban environments where visual considerations are important.
Utility companies that aim to maintain the visual appeal of cityscapes may choose these cables as a suitable option, ensuring that power infrastructure blends seamlessly into the surroundings.
While AAC (All Aluminum Conductor) cables have several advantages, they also come with notable disadvantages.
Understanding these drawbacks is crucial for anyone considering their use in power transmission and distribution. Below are the key disadvantages of AAC cables explained in detail.
One of the primary disadvantages of AAC cables is their lower conductivity compared to copper cables. Aluminum has approximately 61% of the conductivity of copper.
This means that for the same cross-sectional area, It will carry less electrical current than a copper conductor.
As a result, to achieve the same current-carrying capacity, It must be larger in diameter, which can lead to increased material costs and weight.
In applications where high efficiency and minimal energy loss are critical, this difference in conductivity can be a significant drawback.
Higher resistance in it can lead to increased heat generation and energy losses, particularly in long-distance transmission lines where resistance accumulates.
This inefficiency may not be suitable for projects with stringent efficiency requirements, making copper a better choice despite its higher upfront cost.
AAC cables are generally not recommended for heavy-load applications. While they can handle typical overhead power distribution loads, their mechanical properties are not as robust as those of other cables, such as ACSR cables, which incorporate steel to enhance strength.
The lower tensile strength of aluminum means that it can be more susceptible to mechanical failure under extreme conditions, such as high winds, ice loading, or physical stress.
In areas where environmental conditions can lead to significant strain on power lines, the use of it may pose risks of sagging or even breaking.
For high-load scenarios, it’s often advisable to choose cables designed specifically for such applications to ensure reliability and safety.
Another disadvantage of AAC cables is their sensitivity to temperature changes. Aluminum has a higher thermal expansion coefficient than copper, meaning that it will expand and contract more significantly with temperature variations.
This characteristic can affect the cable’s tension, leading to potential issues such as sagging or increased stress on supports.
In regions with extreme temperature fluctuations, the mechanical properties of it can be compromised.
The expansion and contraction can cause joints and connections to loosen over time, which may lead to increased resistance and heating at connection points.
Regular monitoring and maintenance may be necessary to ensure that these cables remain safe and effective, adding to the operational costs over time.
While AAC cables are durable, they generally have a shorter lifespan compared to other types of cables, particularly copper. Factors such as oxidation, wear, and environmental exposure can affect the longevity of these cables.
Even though aluminum has a natural oxide layer that protects it from corrosion, this layer can be compromised in certain conditions, leading to accelerated degradation.
In contrast, copper cables, when properly maintained, can often last significantly longer due to their resistance to corrosion and oxidation.
This shorter lifespan of these cables means that utility companies and contractors may face more frequent replacements, increasing long-term costs and disrupting service continuity.
While AAC cables have good thermal conductivity, they can still be at risk of overheating under high load conditions. The lower conductivity of aluminum leads to increased resistance, which can generate heat during operation.
If the load exceeds the cable’s capacity, the heat generated may exceed safe limits, potentially damaging the insulation and the conductor itself.
Overheating can lead to a host of problems, including insulation failure, loss of conductivity, and even fire hazards in extreme cases.
Utility companies must carefully monitor load conditions and thermal performance to prevent overheating and ensure the safe operation of AAC cables.
This monitoring adds another layer of complexity and responsibility to cable management.
The mechanical strength of aluminum is generally lower than that of copper. This difference becomes critical in applications where cables are subjected to significant mechanical stress, such as in regions prone to high winds, heavy snowfall, or ice accumulation.
It may not perform well under such conditions, leading to issues like conductor breakage or excessive sagging. For areas where heavy loads or environmental stresses are anticipated, ACSR cables are often a better choice.
ACSR cables combine aluminum with steel, providing the necessary strength while maintaining a lightweight design.
Choosing the right cable type is essential to prevent mechanical failures and ensure reliability in demanding conditions.
Due to their physical properties, AAC cables may require more stringent installation practices compared to other types of cables. The need for larger diameter cables to achieve the same current-carrying capacity can lead to complications during installation.
Additionally, the potential for sagging and temperature-related expansion necessitates careful planning of cable routes and support structures.
Utility companies may need to invest more time and resources into the installation process to ensure that AAC cables are correctly positioned and adequately supported, increasing overall project costs.
The production and disposal of aluminum can have environmental implications. While aluminum itself is recyclable, the energy required for aluminum extraction and processing is significant.
This process can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation if not managed properly.
When considering the use of AAC cables, it’s essential to evaluate the entire lifecycle of the materials involved, from production through installation to disposal.
Companies committed to sustainability may opt for alternatives that offer a more environmentally friendly profile, weighing the benefits against the environmental costs.
AAC cables are a popular choice for overhead power transmission due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. However, their disadvantages must be carefully considered before making a decision.
Key drawbacks include lower conductivity compared to copper, which can necessitate larger cable sizes for equivalent performance, and limited mechanical strength, making them less suitable for heavy-load applications.
Additionally, It can be sensitive to temperature fluctuations, potentially leading to sagging and mechanical stress over time.
While they offer advantages such as cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, their shorter lifespan and risk of overheating may result in increased long-term maintenance and replacement costs.
Ultimately, the choice to use these cables should be based on a comprehensive assessment of specific project requirements, including load capacities, environmental conditions, and overall cost-effectiveness.
By understanding both the benefits and limitations of it, engineers and project managers can make informed decisions that ensure the reliability and safety of electrical systems in various applications.